| 🛠 | This subject is work in progress. Please bear with us while improvements are being made and assume good faith until the edits are complete. For information on how to help, see the guidelines. More subjects categorized here. |
🛠 |
Phonetic System's Characteristics
Unlike previous English and Japanese Vocaloids, the Korean engine is only partially based on X-SAMPA notation. This is due to the nature of hangul, which already functions as a phonetic alphabet. The voicebank's coding uses romanized hangul for the consonants and X-SAMPA based coding for the vowels. A possible reason why romanization is used for the coding of the consonants is due to the Korean language's many allophones. Non-native speakers will find the Korean Phonetics are more complex then either English or Japanese to work with and it is essential that they study how to the Korean language works when using the engine.
In total, the Korean language has 26 initial consonants, 7 final consonants, and 16 vowel sounds of which the entire language is based upon.[1]
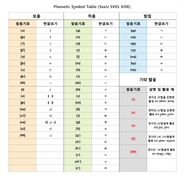
Vowels
Diphthongs
Consonants
Non-Native Phonemes
Unlisted Phonemes
Within SeeU's voicebank are multiple phonemes that, while unlisted in the chart provided by SBS, produce audible results to some extent. It's speculated that these extra phonemes were originally intended to be included to expand the voicebank's language capabilities, but due to time restraint were never completely recorded. It is unknown if future Korean language voicebanks will include these phonemes.
- [T]
Consonant. Produces audible results when placed after a vowel. V-C transitions were recorded, but the voicebank lacks C-V transitions for this phoneme. Most likely meant to be the same sound it represents in English voicebanks. Produces a more lisped sound similar to the [s] phoneme.
- [D]
Consonant. Audible results vary; Some V-C and C-V transitions are present depending on the connecting vowel. Produces a shorter sound similar to the [Np] phoneme.
- [dz]
Consonant. No audible sound. Produces the same results as the [N] phoneme or [Sil] in other voicebanks.
- [lp]
Consonant. Audible results vary. Most likely intended to be the equivalent of [l] in english voicebanks, due to it already being used to represent a different sound in Korean.
- [Q@] [e@] [I@] [O@] [U@]
Rhotic Vowels. Audible results very minimal. Only works when between two other phonemes. Most likely meant to be the same sounds each represents in English voicebanks. Produces very glitched noise.
Positional Allophones
Consonant Assimilation
When entering notes with hangul input, the Vocaloid 3 editor automatically detects and edits the phonetic values for cases in which consonant-to-consonant assimilation occurs. However, a flaw with this system is that the editor changes phonetic values regardless of the distance between notes. For example, "언어" (language) entered into the editor will produce [7][n 7]. However, when the two syllables are seperated with a pause inbetween, the correct pronunciation should be [7 np][7]
Vowel Assimilation
Like Japanese, consonants in Korean become palatalized before /i/ and /j/. However, unlike Japanese, Korean consonants also become labialized before /o/, /u/, and /w/ as well.
Table
| Symbol | Classification | IPA Symbol / Name | Sample Hangul / RRoK | Notes | Related Phonemes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [a] | vowel | a | ㅏ (a) | Closer to /ɒ/, but /a/ is used for traditional notation | |
| [ja] | vowel | ja | ㅑ (ya) | ||
| [7] | vowel | ɤ | ㅓ (eo) | Proper notation of ㅓ is frequently debated. More commonly it is transcribed as /ʌ̹/ or /ɔ̜/ | |
| [j7] | vowel | jɤ | ㅕ (yeo) | ||
| [e] | vowel | e | ㅐ(ae), ㅔ (e) | Younger speakers do not differentiate between ㅐ and ㅔ, which are more correctly pronounced /ɛ/ and /e/ | |
| [je] | vowel | je | ㅒ (yae), ㅖ (ye) | ||
| [o] | vowel | o | ㅗ (o) | ||
| [oa] | vowel | wa | ㅘ (wa) | ||
| [jo] | vowel | jo | ㅛ (yo) | ||
| [u] | vowel | ju | ㅜ (u) | ||
| [u7] | vowel | wɤ | ㅝ (weo) | ||
| [ue] | vowel | we | ㅙ (wae), ㅞ (we), ㅚ (oe) |
ㅚ is traditionally pronounced /ø/ however in South Korean speech it has become /we/ or /e/ |
|
| [ui] | vowel | wi~ɥi~y | ㅟ (wi) |
Usually /y/ or /i/ before ㅅ ㅈ and ㅊ /wi/ or /ɥi/ elsewhere |
|
| [M] | vowel | ɯ close back unrounded vowel | ㅡ (eu) | ||
| [Mi] | vowel | ɰi | ㅢ (eui) | ||
| [i] | vowel | i close frount unrounded vowel | ㅣ (i) | ||
| [g] | initial consonant | g~k velar plosive | ㄱ (g) |
Pronounced /k/ at the beginning of a sequence or after /k̚/ /t̚/ or /p̚/ pronounced /g/ elsewhere |
[g'] [gp] |
| [g'] | initial consonant | k͈ | ㄲ (gg) | Tense /k/ |
[g] [gp] |
| [n] | initial consonant | n alveolar nasal | ㄴ (n) |
[np] | |
| [d] | initial consonant | d~t alveolar plosive | ㄷ (d) |
Pronounced /t/ at the beginning of a sequence or after /k̚/ /t̚/ or /p̚/ Pronounced /d/ elsewhere |
[d'] [dp] |
| [d'] | initial consonant | t͈ | ㄸ (dd) | Tense /t/ | |
| [r] | initial consonant | ɾ alveolar tap | ㄹ (r) | Intervocalic ㄹ | |
| [l] | initial consonant | l lateral alveolar | ㄹ (l) |
Occurs only when initial ㄹ follows ending ㄹ |
|
| [m] | initial consonant | m bilabial nasal | ㅁ (m) | ||
| [b] | initial consonant | b~p bilabial plosive | ㅂ (b) |
Pronounced /p/ at the beginning of a sequence or after /k̚/ /t̚/ or /p̚/ pronounced /b/ elsewhere |
|
| [b'] | initial consonant | p͈ | ㅃ (bb) | Tense /p/ | |
| [s] | initial consonant | sʰ | ㅅ (s) | Laminal "s" | |
| [sh] | initial consonant | ɕʰ | ㅅ (s) |
Palatalized ㅅ. Only works before /i/ or /j/ |
|
| [s'] | initial consonant | s | ㅆ (ss) | Apical "s" | |
| [sh'] | initial consonant | ɕ voiceless alveolopalatal fricative | ㅆ (ss) |
Palatalized ㅆ. Only works before /i/ or /j/ |
|
| [N] | initial consonant | ʔ glottal stop | ㅇ(-) |
Silent initial consonant. Glottal stop when between two vowels |
|
| [c] | initial consonant | ㅈ (j) |
Pronounced /tɕ/ or /ts/ at the beginning of a sequence or after /k̚/ /t̚/ or /p̚/. Pronounced /dʑ/ or /dz/ elsewhere |
||
| [c'] | initial consonant |
t͈ɕ ts |
ㅉ (jj) |
Tense /tɕ/ or /ts/ |
|
| [ch] | initial consonant |
tɕʰ tsʰ |
ㅊ (ch) | ||
| [k] | initial consonant | kʰ | ㅋ (k) | ||
| [t] | initial consonant | tʰ | ㅌ (t) | ||
| [p] | initial consonant | pʰ | ㅍ (p) | ||
| [h] | initial consonant |
h~ɦ voice(less) glottal fricative ç voiceless palatal fricative ɸ voiceless bilabial fricative x voiceless velar fricative |
ㅎ (h) |
Contains many allophones: /h/ at the begining of a sequence /ɦ/ intervocalically or after a voiced final consonant /ç/ before /i/ or /j/ /ɸ/ before /u/ /w/ or /o/ /x/ before /ɯ/ Presence of allophones vary greatly from speaker to speaker. |
|
| [@r] | vowel | ɚ rhotic schwa | singer, roller | Non-native to Korean | |
| [C] | initial consonant | sʲ | sister, recieve |
Works only before [i] While [C i] and [s i] are identical phoneme-wise, the first has smoother transition and the latter does not work at the begining of a sequence. |
|
| [z] | initial consonant | z voiced alveolar sibilant | zoo, zero | Non-native to Korean |
[s] [C] |
| [f] | initial consonant | f voiceless labiodental fricative | father, family | Non-native to Korean | |
| [v] | initial consonant | v voiced labiodental fricative | value, voice | Non-native to Korean |
[b] [f] |
| [gp] | final consonant | k̚ unreleased velar plosive | ㄱ (k) | Unreleased plosive |
[g] [g'] |
| [np] | final consonant | n alveolar nasal | ㄴ (n) |
[n] | |
| [dp] | final consonant | t̚ unreleased alveolar plosive | ㄷ (t) | Unreleased plosive |
[d] [d'] |
| [rp] | final consonant | l | ㄹ (l) |
[] [] | |
| [mp] | final consonant | m bilabial nasal | ㅁ (m) |
[m] | |
| [bp] | final consonant | p̚ unreleased bilabial plosive | ㅂ (p) | Unreleased plosive |
[b] [b'] |
| [Np] | final consonant | ŋ velar nasal | ㅇ (ng) |
Gallery
See also
- Conversion Lists
- Interwiki articles
- Korean Phonology (Wikipedia)
- IPA for Korean (Wikipedia)
External links
- Korean Phonetic Symbol Table (Phoneme list of SeeU's Korean voicebank)
Refererences
| ||||||||||||||||||||